| Art Q&A > Archeology |
|
|
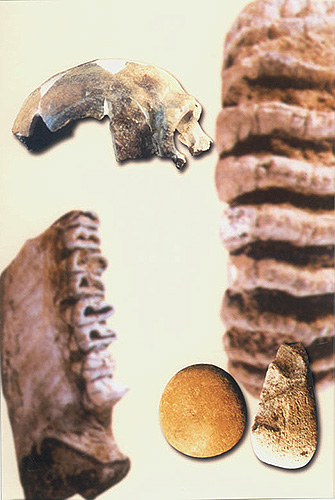
Site of the Maba Man
Location of human fossils of the Mid Paleolithic Age
Location: Qujiang County, Guangdong Province
Period: 129,500-135,000 BP
Excavated in 1958
Significance: The find is of great significance to the study of the evolution of human physical development in south China.
Maba Man was an early Homo Sapiens of the middle Paleolithic Age. The skull fossil found here belonged to a middle-aged man. The skull had very coarse superciliary arches and an extremely contracted orbital surface. The frontal bone was longer than the parietal bone. All these indicate the primitive character of Homo Erectus, although the skull had thin walls and the brain was larger than Beijing Man. Thus, it has been classified as Homo Sapiens. Actually, this individual represented a transitional state from Homo Erectus to early Homo Sapiens. These remains can be dated between the Middle and Late Pleistocene Epochs -- about 200,000 to 100,000 years ago.
In the same cave where Maba Man was discovered, a large quantity of animal fossils of the Fourth Ice Age has been unearthed. |
||||
All rights reserved. Reproduction of text for non-commercial purposes is permitted provided that both the source and author are acknowledged and a notifying email is sent to us. |
||||
 |
 Introduction
Introduction